I have written extensively on this site about edible flowers, both cultivated and wild. Here 98 previous separate entries about cultivated flowers are in one spot. So if it seems you have read parts of this before, you might have. However, this focus is just on cultivated flowers.

It’s difficult to imagine a kitchen or herbal medicine cabinet without Angelica around someplace. Angelica has long been valued for its seeds, stems, leaves and shoots. The first two for flavoring — such as in Chartreuse — and second pair as cooked greens, particularly in the Izu Islands of Japan where there are a favored addition to springtime tempura. They have a celery-like flavor. North American Indians, however, smoked the leaves for medicinal purposes. Celery-ish may its green parts be the blossoms however have a light anise flavor.

Artichoke blossom
If I don’t include artichokes among the edible flowers several will gleefully write and tell me I missed one. No doubt I have missed many. That said we really don’t eat the blossoms of the artichoke. They are actually bitter but if you want to have at it. We eat the floral bracts, read fat leaves below what will become the flower. We eat them raw, boiled, steamed, baked, fried, stuffed, and marinated. When marinated they are called artichokes hearts. In Europe they are dried and used in soups. The inner portion of the flower stalk is also edible, much like true thistles. The flowers themselves are used for a substitute for rennet, meaning they will curdle milk. I said they were bitter. Young artichoke leaves are fed to snails to improve their flavor. Yum. Artichokes have been around for a long time. Zeus (said Zeff in Greek) turned a scorned lover into an artichoke. It doesn’t pay to irritate a god. And young Norma Mortenson got her start in 1948 when she became the first “Artichoke Queen.” You know her as Marilyn Monroe

Arugula blossoms are peppery
Among the more peppery blossoms of the garden is Arugula, also called rocket and roquette. It’s a popular aromatic salad green grown for its leaves but also its seeds. Somehow the blossom gets overlooked… well, not in my kitchen. Arugula is one of those garden vegetables that is also very easy to grow in a patio pot and lasts for many months with repeated cuttings. Though a forager I have grown arugula in my gardens for many years. When the plant finally wants to go to seed you can prolong it by harvesting the flowers. Then enjoy the seeds. Greeks call Arugula Roka.

Bachelor Buttons, spicy and cloves
When you’re a kid you’re told everything is poisonous, and for me that included Bachelor Buttons. Also called the cornflower, they have been tossed into salads and used for a garnish for a long time. They got the name cornflower because the hardly species grew in English grain fields, and corn once meant any grain. Long before wedding rings were common bachelors indeed did wear a cornflower in a jacket button hole to let the ladies know they were single. How did she let them know the same thing? Curiously, she showed cleavage. Married women covered up, single women advertised. Another version is that if the flower retained it color while worn his love was true, but if it faded it was not… sounds a bit rigged to me… Then again, I might not have been a lifelong bachelor if I had picked a few of these. Bachelor’s Buttons were the favorite flower of President John Kennedy. His son John John wore one at his wedding to honor his father. The flower also reaches back into history in that it was used in the funeral wreath made for Pharaoh Tutankhamun, about 3,300 years ago. Their flavor is spicy, sweet, reminds one of cloves.

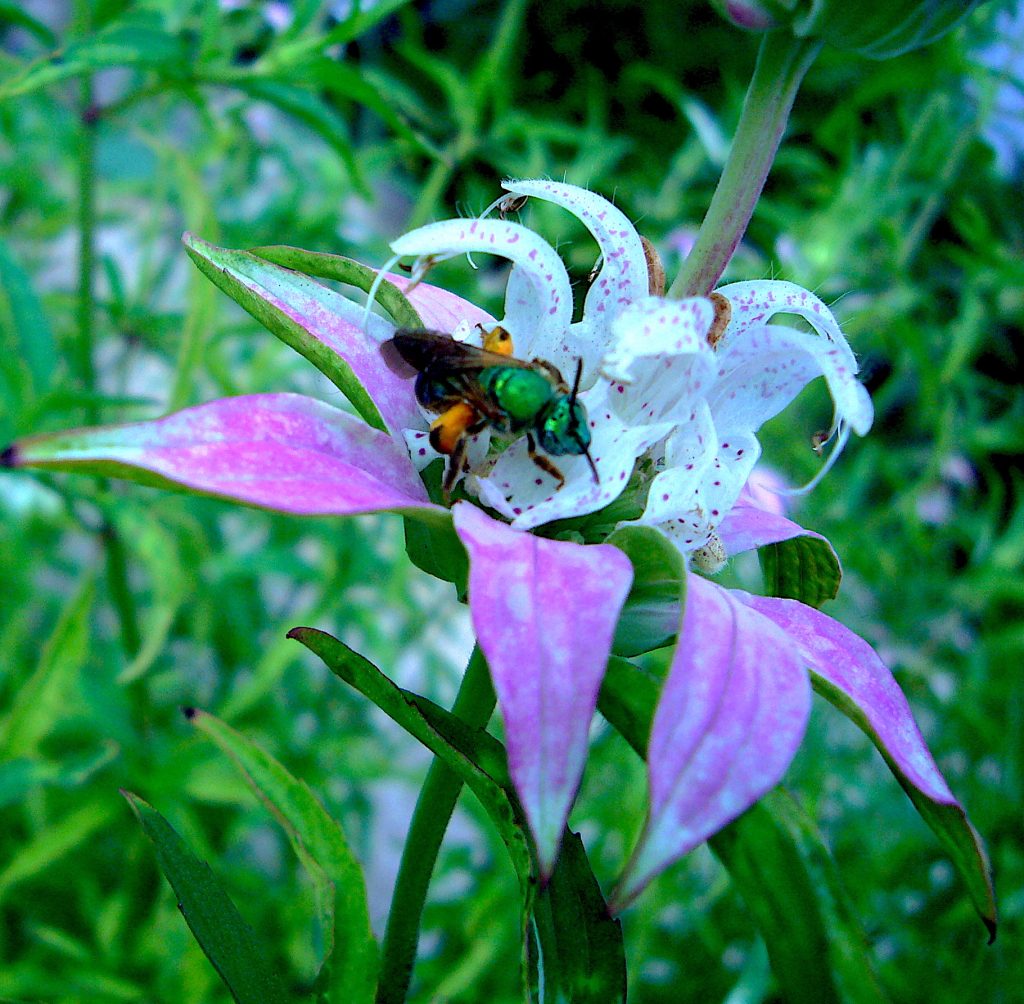
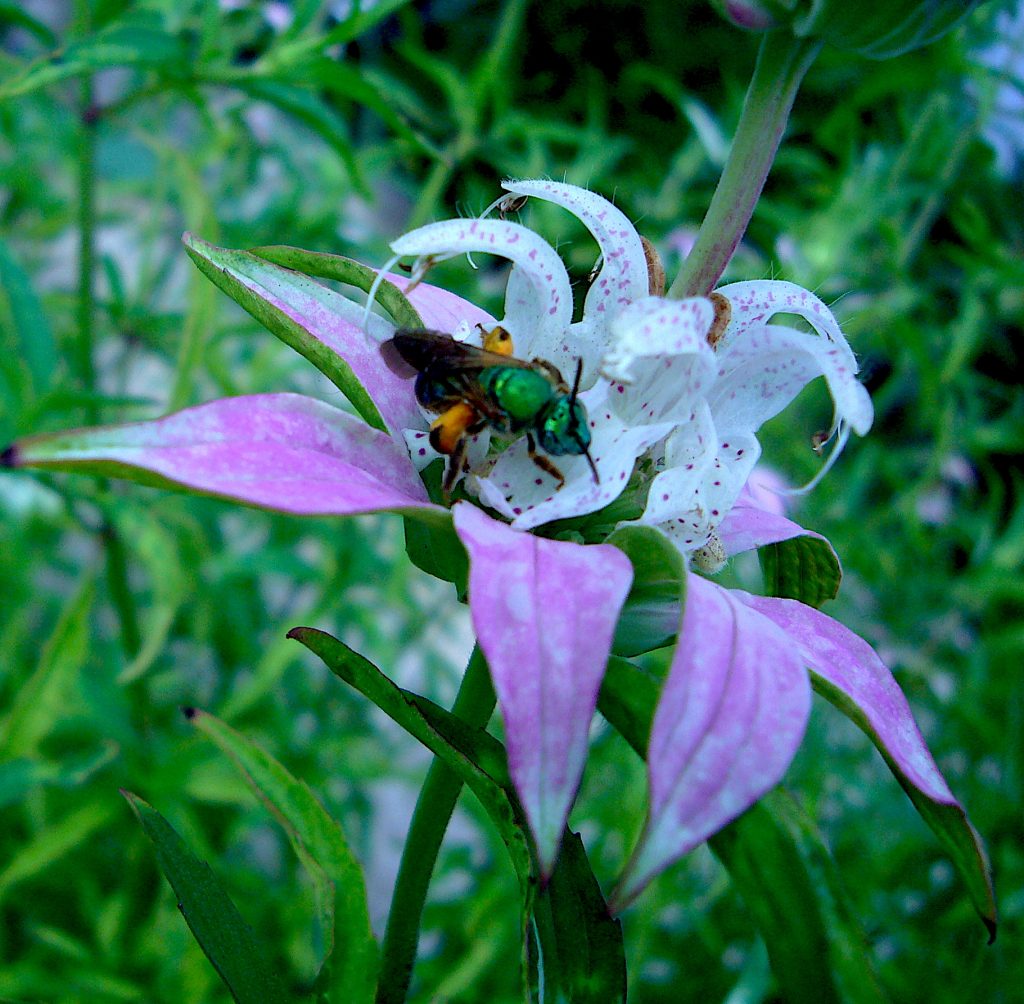
Baloon Flower and Bee
Let’s start at the bottom and work up. Our next plant is known for its root. In the greater Campanula clan, the root of the Balloon Flower, Platycodon grandiflorus, is very popular in Korea where it is cut into strips, seasoned with chilis, vinegar, sesame oil and soy sauce and eaten as a salad (which also tells you you can can get the root still alive in Korean markets, plant it, and get blossoms.) It is also used in soups, stews, dishes with vinegar, and is one of the ingredients in Toso, or sweet Japanese sake. Boiled young leaves are eaten in salads. Its blossoms are sweet in taste, have a bit of texture, and are used in salads, stuffed, candied or dipped in butter. The Balloon Flower is so called because before the petals open are fused at first making the blossom look like a balloon.

Few people in temperate North America ever think of eating a Banana blossom, but a lot of folks in warm areas do, and it does not prevent your banana tree from producing fruit. The entire flower/fruit arrangement of the Banana is odd with the blossom being a purplish torpedo. Look closely at the stalk end of the blossom and you can see what will eventually become a hand of Bananas. The blossom can be eaten raw (bitterish) or cooked, less or no bitterness. Usually it is peeled to get the more tender parts then shredded or sliced thin and soaked to reduce the bitterness. The flavor is not of the Banana but rather more of a vegetable.

Baobob Blossom
With so many readers around the world I have to include an exotic or two though this next flower does grow in Florida and other warm areas. The Baobob Tree, Adansonia digitata, is extremely odd looking and versatile. Like the Kapok tree it is pollinated by bats. The fruit is eaten, the leaves boiled as a potherb or dried and ground and used like file, to flavor and thicken sauces, stews and soups. The seeds are used as a coffee substitute or as a baking powder substitute. Germinating shoots and tender shoots are eaten. And the flowers are edible raw.

I will admit to being lazy and throwing Basil blossoms into my pesto, and soups and stews. That workhorse of the kitchen and Italian cuisine has edible flowers s why not use them. It was a practical matter besides culinary. At some point your Basil plants begins go to blossom. It’s making enough energy to reproduce and send forth seeds. If you let it, the bush senses its purpose is over — no doubt a chemical signal — and retires. But if you keep snipping off the blossoms it keeps on living to reproduce another day. By using the Basil blossoms you get more Basil leaves. The blossoms are usually white but can be pink to lavender. They taste like basil lite, a nice salad sprinkle.

Bauhinias since first discovered have been a pain to sort out, and now there are some 600 species in a variety of colors. The blossom of the Bauhinia variegata and Bauhinia purpurea are eaten raw, pickled or cooked as a vegetable. Some Bauhinia blossoms are used for their nectar. Check out your local species with a an expert as they are quite varied in use. My friend Sunny Savage, resident of Hawaii and now sailing about the world, uses Bauhinia blossom raw in salads. Often called the Camel Foot Tree because of the shape of the leaf, Bauhinias are also known as the Orchid Tree and the Hong Kong Orchid Tree.

Bee Balm, a Monarda, is another huge selection of flowers closely related to the mint family. Intense, aromatic, the flavors can vary not only species to species but between cultivated specimens and their wild siblings. The leaves are often used to make tea, some with calming qualities. Often the entire plant is placed in the house to give a pleasant aroma as it dries. The blossoms tend to reflect the flavor of the parent plant but usually have hints of oregano to thyme to citrus flavors.

My video and separate article on Begonias got me mentioned in the national New Zealand magazine about them. It’s a small electronic world. Begonia blossoms are edible raw or cooked, as are the leaves of most of the Begonias, particularly the Wax Begonias. The flavor, like the tulips, varies with the color. It can range from swampy to sweet. The biggest problem you are going to run into with begonias is since they are usually cultivated they are also sprayed with pesticides if not other materials. You either have to raise them specifically to eat or be a lazy gardener. Either will do. Fortunately for me, and not for the state of Florida, Begonias have become naturalized so I can find them in the wild. Indeed, it was some 20 years ago when I was canoeing on Rock Spring Run — read in a swamp — when I saw a Begonia and wondered what it was doing in the modern urban equivalent of the middle of nowhere. The leaves reduced to a paste and mixed with sour cream, a little sugar, and then baked make a delicious tartlet. And of course, the blossoms are an attractive and tasty addition to salads.

Black Salsify
Edible plants collect a lot of names. This one has been dubbed Black Salsify, Spanish salsify, black oyster plant, serpent root, viper’s herb, viper’s grass, and simply Scorzonera which is also its botanical name, Scorzonera hispanica. A native of the Mediterranean areas it’s cultivate around the world and happens to be naturalized in California. It was cultivated in Europe by the 1600s and is a significant crop there still. The root contains it contains protein, potassium, calcium, phosphorus, iron as well as vitamins A, B1, E and C. It also has inulin which is suitable for diabetics. The long black roots are boiled, steamed, baked, batter-fried, put into soups and stews or roasted as a coffee substitute. Shoots are added to tossed salads. Flower buds raw or cooked are eaten on salads. Blossom petals are also sprinkled on salads or used in omelettes.

I do believe I was the first to publish anywhere in modern times, Internet or otherwise, that Blue Porterweed blossoms are edible. Even the Cornucopia II venerated doesn’t mention it. No doubt their edibility was known long ago because the flower has been used for at least a few hundred years to make tea, beer and as a flavoring. I am sure somewhere along the way someone tried the flowers. Locally we have two versions, a native which grows low, and a tall cultivated one. The flowers on both are edible, and the odd part is they taste like raw mushrooms. As with many delicate flavors the nose is quite involved and it takes a few moments for the flavor to come through. Tasters find it amazing. The flavor does not survive cooking. Incidentally, the leaves are used to make a tea and beer and the stem is used for flavoring.

Where I live there are only two plants that smell like cucumber. One is a wild cucumber. The other smells like cucumber but does not taste like cucumber. But you can also cultivate a flower that has the faint taste of cucumber, Borage. While it is naturalized in southern Europe most of us have to put it in our herb garden. Borage has a long history of medicinal and culinary use. Currently it is a source of gamma linolenic acid, GLA. The sweet blossoms and leaves have the taste of cucumber. The flowers are often used in salads or as a garnish and do well in many drinks. One technique is to put the blossoms in an ice cube tray and freeze them into ice cubes to be used in drinks.

Calamint
Think mint. Now think oregano. Put them together, mint and oregano and you have the Lesser Calamint. Important to Italian cooking, it is an old world plant found in flower gardens and a smattering of states from the Old South northeast to New York. Hardy perennial to two feet. It is said to be indispensable in bean and mushroom dishes. The regular Calamint (Calamintha grandifolia) also has edible blossoms as well though its flavor is a cross between mint and marjoram, read not quite as strong. They have been cooking with it in Roman since the Romans, particularly meat dishes. Toss the pink to lavender blossoms in salads or use to flavor dishes.

Calendula has been called the poor man’s saffron. There are 12 to 20 species in the family, depending on who is counting. They are native from Micronesia to the Mediterranean area to Iran. Often lumped in and confused with marigolds — which can be used for coloring — the name Calendula comes from the Latin kalendae, meaning the first day of the month, and where we get the English word calender. It is believe they are called that because in warm regions they are always in bloom and always on the first day of every month. The Calendua’s flavor is similar to saffron, bitter to tangy.

Clustered Bellflower
Campanulas are not a small clan. There’s some 500 of them in the genus. Some are eaten for their roots, leaves or flowers. The rampion, or Campanula rapunculus was widely grown in Europe for its radish-like roots and leaves. In fact, “rapunculus” is dead Latin for “little turnip” and was the Brothers Grimm’s inspiration for the fable name Repunzel. The Clustered Bellflower, Campanula glomerata, has bluish flowers that are eaten raw. They are sweet in flavor as are their leaves. Usually used in salads. Campanula punctata flowers and leaves are cooked like a potherb. Campanula rapunculoides, Rover Bellflower, roots and leaves are eaten (remember, in dead Latin -oides means looks like or resembles. So the C. rapunculoides looks like the C. rapunculus.) In parts of Greece the Campanula versicolor, Variously Colored Bellflower, are eaten and cooked like a vegetable. The leaves are used in salads and taste similar to peas. The flowers are also very good.

Carambola, Star Fruit
I happen to have the next tree growing in my back yard. It flowers twice a year but the second setting is minor. Called Carambola or Star Fruit, its botanical name is Averrhoa carambola. Known for its edible fruit, which go from green and tart to golden yellow and very sweet. But, it also has edible flowers and leaves that are used like sorrel. The acid flowers are used in salads or used to make conserves. The fruit is eaten fresh, dried, sliced into fruits and salads, or used in sherbets, ices, creams mousses and other desserts. The tart fruit are cooked fish and fowl or made into a relish. Another member of the genus, Averrhoa bilimbi is the cucumber tree. It’s fruit and flowers have various edible uses.

There are few flowers more common than Carnations. They have been cultivated since ancient times and were quite popular in Rome during the empire days. Its botanical name, Dianthus, means flower of the Gods. Originally just in shades of pink or peach now a rainbow of carnations are available, each still keeping it clove-like scent. Like many blossoms Carnations were used to convey sentiments in times when overt expression of love were frowned upon. Thus many a bouquet was carefully constructed to send just the right message with just the right color.

Cantip
Most cats love it, a few don’t. The difference is genetic. The active chemical is Nepetalactone. It’s a mild hallucinogenic that produces euphoria in many cats. In humans it makes you sleepy, like chamomile though in large amounts it is emetic. Catnip (Nepeta cataria) is an herb of the mint family and at one time was spice found in the kitchen. Although a native to Europe, it has been exported to the rest of the world and in some places is considered a weed. It is naturalized in every state except Florida and all the first tier Providences of Canada. Even though it is considered a weed most folks still think of it as a cultivated plant because most buy it for their cats. Indeed, growing catnip can be a problem because feral cats and domestics on the roam won’t leave it alone. When protected catnip grows to about a yard high, branches much, and is topped by small white flowers with purple spots, a common trait of the mint family. The leaves can be candied or brewed into a mint-like aromatic tea. In Europe the leaves and young shoots are put into salads or seasoning for sauces, soups and stews. While the flowers can be sprinkled on salads they are usually used to make tea, often along with leaves. Catnip is also high in Vitamin C.

Three a.m. has to be the absolute worst time of any day. And when I’m awake then I make myself a cup of Chamomile tea. The small flowers taste like the tea, on the sweet side and apple-ish. In a publication North Carolina State University warns that the flowers contain “thuaone” but that is a misprint which has since been proliferated over the Internet. I don’t cut and paste. I do my own research and write every word myself. That’s why there are so many typos. Chamomile has very low amounts of thujone, which is credited in significant amounts to getting people high. It’s one of the compounds in Absinthe. I’ve had Absinthe in Greece and the liquorish liquor did nothing for me. All Chamomile tea does for me, and most, is make me sleepy. If you are allergic to ragweed, however, you might want to avoid Chamomile. The two plants are related and Chamomile can bother some people with a ragweed allergy.

One of my favorite dishes used Chervil as a flavoring. In a casserole you put alternating layers of thinly sliced potatoes and sliced onions, a layer of one then a layer of the other. You would dab each separate layer with real butter and then a pinch of tarragon and a sprinkling of Chervil. Then a bit of salt and pepper on each layer to taste. You fill the casserole that way. On top you spice it up one more time, add more butter, and a sprinkle of paprika. Into the oven it would go until tender. It also made great hash. The Chervil was a subtle flavor, and loses much to heat. That is why when you use the flowers for flavoring in a dish or a salad you add them last, in a dish just enough to heat, in a salad just before serving. Their anise flavor is subtle but the nose knows all.

I can remember the first time I saw Chicory in blossom. I was in Alexandria, Virgina, visiting a dear friend for a couple of weeks and wandering amongst parks, monuments, and museums. The mower had somehow missed it and I noticed it immediately. The blue pretty Chicory is a close relative of the dandelion but not sweet at all, In fact it runs towards bitter and earthy. Think radicchio. You can eat the flowers and the bud, or pickle the buds. The root has been roasted and used to extend and flavor coffee.

Our next edible needs little introduction, the Chrysanthemum, also called Mums, one of my grandmother’s favorites. First cultivated in China perhaps 3,500 year ago, they have been on the menu for many millennia. Mums got to Japan in the 8th century and are the flower of the emperor’s family. Yellow and white “mums” Chrysanthemum morifolium, are the ones usually used in the kitchen. The blossoms are boiled to make a sweet drink. In salads the raw flowers are pungent, if not bitter. Use sparingly. They are also used to flavor wine (remember lilac wine?) The leaves are steamed or boiled and used as greens. I’ve grown them in my vegetable garden for that very purpose. The greens also dehydrate well.

You either like Cilantro, or you don’t. If you do like Cilantro then the flowers are Cilantro lite. The plant has a dual identity. The green part much used in Vietnamese cooking is called Cilantro. Its seeds however are called coriander. Cilantro sparks intense debates. To some people it tastes like soap. The famous chef of French cooking, Julia Childs, said she would take Cilantro out of a dish and throw it on the floor. Others enjoy the flavor. The different perceptions apparently is one of association. The more one is exposed to Cilantro the more it moves from soap to food. It grows on you. While its seeds, coriander, are quite aromatic they don’t seem to engender flavor disagreements like the leafy parts of the plant.

Citrus, use sparingly
For the home crowd one has to mention Citrus blossoms. Orange blossoms, lemons, grapefruit, calamondins, kumquat… The whole citrus club. They are, no surprise, citrusy and in fact the flavors are used often in Mediterranean cooking. When I first moved to Florida back in the Dark Ages I can still remember the first time I detected the wonderful aroma of a citrus grove in blossom. I thought it was Mayflowers, a blossom from my past.

Clary Sage
Clary sage has been in the medicinal bag of tricks for at least 2,400 years. Theophrastus in the 4th century BCE wrote about it. Dioscroides did in the first century CE as did Pliny. A native to the Old World it is naturalized in a smattering of states with no apparent reason. Like many edible flower it is found mostly under cultivation. It’s called “clary” because the sticky seeds were used to help get small foreign objects out of the eye, to help on see clearly. Young and tender leaves are dipped in cream and fried, often eaten with an orange sugar sauce. They can also be dipped in an egg batter and cooked into fritters. The pleasant-flavored flowers are sprinkled on salads.

Dame’s Rocket is a mustard
Dame’s Rocket is a declared invasive species in several places. It’s your civic duty eat the weed. Originally from Eurasia some 400 years ago it’s a mustard that at first glance looks like Phlox. Dame’s Rocket has the typical mustard family four petals, Phlox, five. It’s found essentially everywhere in North America except the Old South. Botanically known as Hesperis matronalis, it is cultivated, escaped and is included in wildbird seed mix. Young leave collected before flowering are eaten like cress. Seed pods can be added stews and soups. Seeds are a source of oil and can be sprouted and eaten. The flowers are used to add spicy flavors to fruit dishes and salads.

A foraging standby in all but the southwest desert and northwest Canada is the Daylily. But first a couple of precautions. I am talking about only the Hemerocallis genus. Also go sparingly, they can be diuretic or laxative. That said day lilies are on the sweet side, vegetable-ish. Like squash and glad blossom they’re used to hold tasty finger food but like other blossoms cut them away from the white bitter base. I used to enjoy them often but the only local patch is now under a highway exit. See full article about them here on sit.

Dendrobium phalaenopsis
If you go to a Thai restaurant often a Dendrobium phalaenopsis is put on your plate. No that not a creature, its an orchid unfortunately without a common name in English. Said Den-DROH-be-um fal-en-NOP-siss their flavor is light, if any, but they are pretty with a crisp texture. This also brings up the debate if all orchids are edible. Personally I think that is impossible for one person to say as there are more than 20,000 of them, maybe 26,000, in some 800 genera. I’m not sure one person can know them all. Many do have edible roots. Edible flower information is sketchy. One would like to think orchids used as garnishes would be edible just to avoid liability. However garnish writers seem to skip over issues of orchid edibility. Kinda like writing about flying and leaving out the airplane. Dendrobium phalaenopsis come in a variety of colors and are native to southeast Asia. They are not difficult to grow. Use in salads and as a garnish.

As is often said, travel is a broadening experience. When you go to a different land it’s exciting to see plants you don’t know specifically but you know what family they are in. The first time I went to Greece I saw wild Dill growing everywhere, besides wild figs. Then years later on a business trip to extreme south southern California there was dill again. Wouldn’t you know I happen to live in a state where it’s not found in the wild. Oddly Dill blossoms are stronger flavored than the leaves. Tangy, use the flowers as you would the herb and seeds.

Durian Blossoms
This next tree is infamous for its fruit. You either wildly love its aroma or passionately hate it. Carrying it on trains in Thailand is illegal. It is banned from commercial flights. At least one jet passenger was stopped and a man reeking of it kicked off. Last year a tycoon sent a private to pick up 88 fruit when it came into season. He wanted 100 but they weren’t availabe then. It is the infamous Durian, a spine-covered fruit that smells like a sewer and tastes like microwaved socks, and some people love it. Their passioin is not shared. The flower petals are edible. Did I mention the huge fruit also has killed people falling from the tree and hiting them on the head.

Many a hibiscus flower can go into salads and the like but I don’t know how many I’ll cover because most of them are virtually flavorless but they are pretty and add texture. I happen to like the False Roselle, Hibiscus acetosella, because beside the edible pink flower the leaves are edible as well, raw or cooked. I use the young leaves for salads and stir fry. They keep their color. A close relative, Hibiscus sabdariffa is the real roselle and is also known as the “Florida Cranberry” or the “Cranberry Hibiscus.” A tart juice can be made from its fat calyxes. Its blossoms are edible as well.

Another plant I saw growing wild in Greece but is mostly cultivated in the United States is Fennel. In fact, at one mountain pass not far from Sparta the only weed growing in the crack of the curb along the road was fennel, and most of it close to a yard tall. I’ve always included Fennel in my garden because it’s so versatile. Fennel’s blossom is an explosion of yellow and the flavor is of mild Fennel. It’s the hint of anise appreciated in cold soups and many desserts. Incidentally, Fennel is the only species in its genus, Foeniculum vulgare.

Forget-Me-Nots
The story I heard from my mother, not the best source of romantic literature, was that he was in Alaska and braved rushing waters to get some wild flowers she requested. He got the flowers but was swept away by the current and as he was about to meet his watery fate he yelled “Forget Me Not.” Hmmmm… Guy dies, woman doesn’t get flowers, has to walk home alone where she meets Paul Bunyan… Let’s start with the fact Forget-Me-Nots aren’t native to Alaska but they are in England and… In exile in 1398 Henry IV adopted the flower as his symbol and retained when he returned from the hinterlands a year later. Perhaps that is why historically Forget-Me-Nots represent faithfulness and enduring love. They are found sporadically in the wild in the northern half of North America and cultivated elsewhere. As most folks see them only in gardens we’ll call them cultivated though surprisingly they are invasive in Wisconsin. Botanically Forget-Me-Nots are Myosotis sylvatica, which means Mouse Ear of the Woods. Properly they are Wood Forget-Me-Nots. Five petals, flat face, a yellow eye, usually blue but can be pink to white. The blossoms are added to salads as a garnish and make excellent candied blossoms.

It’s easy to spot the Forsythia in the spring time. Just look for a naked shrub covered with yellow blossoms. You can find them in most urban areas and they escaped cultivation is several locations. The blossoms are spicy, minty, and slightly bitter. They add a cherry garnish to salads, particularly after a long winter. Very young leaves… very young leaves… are edible raw. Better boiled. The enduring argument regarding the Forsythia is who is it named for. See a separate article on site.

Fragrant Water Lily
One of the more difficult things about the Nymphaea odorata is what common name to call it. Fragrant Water Lilly and American White Water Lilly seem to be in the running. We’ll go with Fragrant Water Lilly, and it is! Actually the unopened flower buds can be collected and boiled as a vegetable. Once opened the raw blossom can be used as a garnish or nibble. Whether the plant’s rhizome is useful is something of a debate. Some think our local yellow native Nymphaea mexicana can be used the same way.

Freesia blossoms point one way
As a forager one of the first things you learn is that there isn’t much to offer in the Iris family, or, if it is an Iris beware. Freesia is an exception. A native of South Africa and Australia, it’s an Iris to about 18 inches tall and grows from a bulb. The stem branches once giving it a classic Y shape. One odd thing about the Freesia is that they grow in a helicoid, that is the flowers attach to the stem in a spiral fashion but they all point the same way. Fragrance varies with the variety. And the usual debate is whether it’s a wild plant as it is in its native range or a cultivated plant as most of these readers will find it. I opted for cultivated. So far I have put only one flower in both wild and cultivated and that’s Dame’s Rocket. Freesias colors include white, purple, yellow, orange and red. In the language of flowers they represent “innocence.” The highly scented blossoms are used in salads raw or as a garnish. They are reported to be excellent infused with a sugar syrup, and are used in sorbets for flavoring.

Fritilary’s Bell Blossoms
Originally from China but now grown around the world the Fritillary makes an interesting addition to a flower garden. Soft bell-shaped blossoms with a pale green netting on the outside of the petals and a pale red netting on the inside makes this Lily family member easy to identify. The particular species we’re interested in is Fritillaria verticillata. Their name comes from dead Latin for dice box, fritillus, a reference to the check patttern the veining makes. And while we like fritilaries rodents and deer do not. Young plants, peals and flower buds are eaten after parboiling. They are used in soups or as a herb or cooked with soy sauce. The bulbs are eaten fried or candied. Another members of the genus with edible bulbs is Fritillaria camtschatcensis. The buds might remind you of the Daylily and indeed while in different genera they are botanically standing next to each other. One more point: Do not experiement with fritilaries. The two listed here are known edibles. Others may contain toxic amounts of various alkaloids.

Fuchsia
Discovered by Europeans in the Caribbean in 1703 — the natives already knew it was there — Fuchsia has been an ornamental for centuries. It’s a native of the warmer Americas and parts of New Zealand there’s 110 recognized species now, even some that can grow in cooler climates. Most of them are shrubs though one is known to reach tree height. Fuchsia blossoms are edible as are the peppery grape-tasting berries which grow on long stems. The flower is a favorite garnish because of its many strong colors which can range from white to dark red, purple-blue, and orange. Their flavor is slightly acidic.

You can have a lot of motivation to plant Garden Sorrel. It’s a Rumex and many of the wild sorrels are too bitter to eat, as are their blossoms and seeds. While there are exceptions — I know of only one locally that is pleasant — you can have a steady supply of sorrel leaves and blossoms if you include this old world flavor in your kitchen garden. Rumex acetosa is used in nearly every ethnic cuisine in Europe, from being mixed into mash potatoes to flavoring reindeer milk. The blossoms are tart like the rest of the plan, lemony. Use as you would a lemon.

Is there a flower garden in America without a Gardenia in it? They are so common they are called the Common Gardenia, Gardenia jasminoides. In dead Latin — all Latin is dead whereas Greek is still alive — –oides (OY-deezs) means “look like” or “similar to.” In this case jasminoides means like the Jasmine and indeed Gardenia blossoms are also used to make jasmine tea. It seems a little like bait and switch but since the pallet doesn’t know the difference your Jasmine tea may be flavored with Jasmine or Gardenia. As for the Gardenia flowers they are eaten raw, pickled or preserved in honey. The fruits are also edible and used as yellow coloring for other fruits.

Because of an early botanical scew up — the first of many — the Geranium group can be confusing. Initally all Geraniums were in one group. But by the late 1700s it was decided they were in two different genus but both were called commonly Geraniums. Got it? Folks have been trying to keep it straight ever since. Generally speaking they fall into two groups, bitter Geraniums usually not consumed, though some can be, and scented Geraniums, whose flowers we can use. The latter genus is Pelargonium. The name comes from the Greek word ????????, pelargós, which means stork because part of the flower looks like a stork’s beak. Scented Geraniums have different scents, among them almond, apple, coconut, lemon, nutmeg, old spice, peppermint, rose, and strawberry. The flowers tend to agree with the plant’s name. They are used in salads, desserts, and drinks.

Ginger Blossoms
Right outside my kitchen window grows Ginger, the kind we get genger root from and use in cooking, Zingiber officinale. I planted it several years ago and when I need Ginger for cooking, I did up a piece. The word ginger comes from French gingembre which was borrowed from Medieval Latin ginginer which was bastardized from the Greek: zingiberis (??????????). Going back further it comes from the Indian subcontinent word inji ver. We just call it good, and a home remedy for motion sickness. Ginger blossoms are gingery and fragrant. They can be eaten raw.

When you live where the ground freezes annually — called winter — you have to wrap some plants and take others inside. That was an annual assignment when I was growing up and on top of the list was digging up Gladiola bulbs every fall. And every year my mother had a huge gladiola garden with boxes of bulbs overwintering in the basement. Had I known gladiola blossoms were edible it might have made the childhood chore more bearable. Glads (Gladiolus) blossoms are bland, lettuce like, and you must remove the anthers… take the middle out. Basically eat the petals. They can also be cooked. Like squash glad blossoms are often used to hold tasty tid bits.

Hollyhocks look great on a plate, and their taste is bland for those who want strong colors rather than flavors. They have also been used to color wine in the distant past when such things were not regulated. The leaves are also edible raw and it’s still a cultivated vegetable in Egypt (the root has starch.) Besides plating and salads you can also make a refreshing tea from the Hollyhock, botanically Alcea rosea and related to the Marsh Mallow. There now many colors to choose from.
 The greater Honeysuckle family is an odd one. It straddles the edible/non-edible line, with some members long used as food and other members at least mildly toxic. For example, elderberries are in the Honeysuckle family, then tend to be edible in North America and not in the Old World. A famous or should I say infamous invasive member of that family is the Honeysuckle, Lonicera japonica, or Japanese Honeysuckle. It’s definitely the one we have here in the south spreading everywhere. Kids have known for generations that you can suck the sweet nectar out of the blossoms. Most of them don’t know, however, that the blossom is edible as well. It has a sweet, honey flavor. You can flavor wine with them as well. Tea is good, too.
The greater Honeysuckle family is an odd one. It straddles the edible/non-edible line, with some members long used as food and other members at least mildly toxic. For example, elderberries are in the Honeysuckle family, then tend to be edible in North America and not in the Old World. A famous or should I say infamous invasive member of that family is the Honeysuckle, Lonicera japonica, or Japanese Honeysuckle. It’s definitely the one we have here in the south spreading everywhere. Kids have known for generations that you can suck the sweet nectar out of the blossoms. Most of them don’t know, however, that the blossom is edible as well. It has a sweet, honey flavor. You can flavor wine with them as well. Tea is good, too.

Horseradish Blossoms
My cousin in southern Quebec… actually first cousin once removed, Beulah Knudson nee Smith, grew the largest Horseradish I ever saw. The winters are harsh thereabouts and that horseradish, Armoracia rusticana, was making the most of their very short growing season. Here in flatland Florida it is too hot to grow horseradish except perhaps in the most extreme northern counties. Most everyone knows that horseradish is a hot root. In fact, the root is rather clever. The two chemicals that make horseradish hot have to be mixed to be hot but the plant keeps them in separate cells so they don’t bother the plant. Only when the cells are crushed together is a hot chemical created. It’s called “horse” radish because “horse” is also used to describe anything big or rough. Young leaves can be added to salads, pickled or cooked as a potherb. Sprouts can be added to salads, or the roots can be cooked as eaten that way. The flowers are edible, quite mild compared to the root. Sprinkle them on salads, throw them in when pickling or cooking string beans and the like.

Hyacinth Bean Blossom
I could almost make an identical entry for the Hyacinth Bean from that of the Scarlet Runner Bean below because they have so much in common and are so unlike other beans. They’re annuals, ornamentals, have edible roots, leaves, pods, beans and flowers. The difference is the Hyacinth Bean seeds themselves have a different toxin that the Scarlet Runner bean and in a greater amount so they have to cooked far longer. The bean-flavored flowers, however, are edible raw or cooked.

I hate to admit it but the only place I can find this next edible flower is in cemeteries because it doesn’t grow in the wild here, Impatiens wallerana. The cultivated Impatiens are from Africa and their blossom is edible, sweet. There is no report of edibility on our native North American Impatiens blossoms raw, called Jewelweed. Indeed, Jewelweed is edible after two boilings but there are no references to any parts edible raw. Just the opposite, all kinds of warning not to eat our native Jewelweed raw. So this is one case of where the cultivated blossom is on the raw food menu but the wild one is not. Jewelweed seeds are edible, small, flavor similar to walnuts.

Italian Bugloss
One cannot make up a name like Italian Bugloss. Also known as Wild Bugloss, Alkanet and Anchusa. Botanically it’s Anchusa azurea a member of the Forget-Me-Not family. Originally from Europe it’s cultivated around the world, is intensely blue, and is used among other things as a dye. Italian Bugloss has become naturalized without logic in a number of places in North America including New Hampshire, Massachusettes, Conneticut, New York, Pennsylvania, Maryland, Ohio. Michigan, Iowa, Texas, Colorado, Utah, California, Whyoming, Idahoe, Oregaon, Washington, and British Columbia The bright blue blossoms are an excellent salad addition and are quite attrative when mixed with rose petals. On Crete it’s called ?????????? ang-GO-gloss-ose. Locals eat the tender stems boiled. Also eaten are the bossoms of Anchusa capensis and Anchusa officinalis. “Bugloss” means ox tongue because of the roughness of the leaves. ?????????? can mean literally “impiety tongue” read rough tongue.

You knew Jasmine was edible. Of course you did. That’s how we get Jasmine flavored tea. But make sure you are getting the right Jasmine, Jasminum officinale not plants in another genus or family falsely called Jasmine. The real Jasmine has tubular white flowers, waxy, and shiny oval leaves. Jasmine is from Asia but because it has been used for so long no one really knows where it got its cultivated start. There are mentions of it in 9th century texts in China and by the 1700s it has spread so well some folks thought it was native to Switzerland. The famous aroma comes from an oil in the petals and it is those petals you use to flavor your tea. If you life in the South do not mistake “Carolina Jasmine” for real Jasmine. It is the offensive and odorous Gelsemium Sempervirens, a significant allergy plant and quite toxic.

I don’t know if I should tell you about Johnny-Jump-Ups or not. Botanically Viola tricolor, they are among the first flowers I can remember my mother picking from the wild and eating on the spot. She did it because her mother did it (and she also never missed harvesting a cowslip either.) Johnny-Jump-Ups like moisture and can tolerate shade so… here goes…. Our house in the country had a septic system and a drain field. That drain field was moist and shaded and Johnny-Jump-Up grew there in profusion. And that is where my mother picked them, one after another, eating them on the spot. She’s now 86. Johnny-Jump-Ups have a mild wintergreen flavor and a variety of uses. They’re added to salads, desserts, soups, served with cheese and used to decorate confections. Incidentally they are the ancestor of the common pansy.

Kapok, Pollentated by Bats
When one studies edible plants you quickly learn that one group can consider a plant only edible, another only medicinal, a third famine food only and a fourth don’t consider it good for anything. The kapok tree, Ceiba pentandra, falls into medicine and food, depending upon the eyes of the beholder. Like the Baobob Tree it is pollinated by bats. Tender leaves, buds and fruit are eaten like okra. Seeds are roasted and ground, eaten in soups, used as flavoring, or employed to make the fermented drink kantong. They can be used to make tempeh or squeezed for cooking oil. Wood ashes are a salt substitute. Flowers are blanched and often eaten with chili sauce, the dried stamens are added to curries and soups for coloring. A nice specimen of the tree can be seen in Dreher Park just north of the entrance to the zoo in West Palm Beach.

Lavender is an old stand-by found in many home gardens including mine. Its flavor is flowery, sweet and citrusy. Lavender has been used to flavor bread, cookies, jelly, beef, wine, sauces, stews, and custards. The blossoms are an attractive addition to champagne. The blossoms are also used around the house to impart a nice aroma from bedding to baths. They is also slightly diuretic.

Lemon Verbena
There is hardly an established garden that doesn’t have a Lemon Verbena in it. A native of South America it was “discovered” in 1785 in Buenos Aires. By 1797 it was the rage of England and has been exported around the world since around 1785. It’s in a well-known association with a lot of plants used for seasoning and antioxidants. The Aloysia triphylla was named to compliment the wife of Infant Carlos de Borbon, Prince of Asturias and son of King Carlos III of Spain. The Infant was a supporter of the arts and botany. Young leaves are eaten as spinach. they are also used to flavor fruit cups, jellies, cold drinks, salads, omletes, salad dressings, and vegetable dishes. The leaves or , tiny, citrus-scented, are brewed into a refreshing tea. Tea from just the flowers is sweeter.

As a kid I never associated Lilacs with food. When the fragrant Lilacs blossomed in late May you knew in a couple of weeks school was soon going to be out for the summer and glorious days were ahead. I don’t think I ever experienced more freedom then those summers. I was a latch key kid so summer vacation meant months of roaming through the countryside for days on end. In the greater Olive family the most common blossom color for lilac was … lilac. My 86-year-old mother in Maine still tends to her Lilacs. And just in case you are interested there is a 10-day Lilac Festival in Rochester N.Y. every May. Not bad for a plant with European ancestry. At the festival they have over 500 different lilacs on some 1,200 bushes. You can even sample lilac wine. Where do I sign up? Lilac blossoms are pungent and on the lemony side.

Lovage
Botanists can’t agree exactly where it came from, though the Old World is close enough for our purposes. Lovage’s beginnings may be humble but it has risen to high esteem for its many usages. Native to perhaps the Mediterranean or southwest Asia Lovage is cultivate throughout Europe and North America. Highly aromatic it is similar looking to flat-leaf parsley only much larger. The flavor is similar to parsley and celery combined with a notes of anise and curry. Botanically Levisticum officinale leaf stalks and stem are blanched and eaten like celery, or peeled and eaten. They can also be candied. Young leaves are chopped and added to salad, soups, stews, seafood, and omelets. The seeds are used for flavoring, often in breads and confections. An aromatic tea can be made from dried leaves or grated roots. And the flowers are edible.

Magnolias are one of the iconic trees of not only the South but exported to many non-hard freeze areas of the world. And people have admired the huge Magnolia blossoms for a long time. Few folks know the blossoms of the Magnolia grandiflora are edible, however their flavor is intense and they taste similar to how they smell. They are not eaten raw per se. They are pickled. Oddly the practice started in England and you only use the petals, not the entire blossom. What works best is to pickle the petals in a sweet/sour pickle recipe. Then take out one petal, dice it, and use it sparingly as a flavoring in salads. The flavor is strong so go easy. Also, M. grandiflora‘s leaf can be used just as Magnolia virginiana‘s can as a bay leaf, that is to flavor soups and the like. However, don’t use the entire leaf because it is way too beg. Cut it into smaller pieces when used like a bay leaf.

Mango Panicle
Did you know Mangos and poison ivy were kissing cousins botanically? And a sensitivity to one can be a sensitivity to the other? In fact there several species related, all in the Anacardiaceae family: Mangos, poison ivy, poison sumac, Brazilian pepper, cashews, and pistachios. You can see the spread, three edibles, one on the cusp of edible/toxic, and two toxics. Some folks might be allergic to all, some to only a couple. Many people get a rash on their mouth after eating mango, called urushiol-induced contact dermatitis. The fruit is originally from India, cultivated for some 4,000 to 6,000 years. It is reported to be the most produced tropical fruit…. yah know…. I question that statistic. I would have thought bananas would have claimed that title. Incidentally, bananas are dying off. Your grandkids may never get to eat a banana. Anyway… when first exported around the world mangos were pickled because of the distances and time involved. In fact “mangoed” became a verb meaning pickled. Mango blossoms grow on long panicles and have a scent similar to Lily of the Valley. Not only are they edible but young leaves as well… as long as you don’t have an allergy. Young leaves and flowers boiled. You can make a natural mosquito repellent by burning dried mango flowers, or use them to make a tea high in tannin. Oh, never burn mango wood. It’s like buring poison ivy. The urushiol gets in the air then your lung then you’re in the emergency room.

There’s a lot of Internet misinformation about Marigolds. All of them are edible from a non-toxic point of view. The more important question is which one have an agreeable flavor? Of them all Tagetes lucida, Tagetes patula, and Tagetes tenuifolia get the culinary nod. Their flavor is citrusy. Usually only the petals are used. No green parts. I also use them for yellow coloring in various dishes. They’re another flower called the “poor man’s saffron” the other being the Calendula.
 Perhaps I have been remiss not mention Mustards more. But they are a huge family and have been touched upon, such as with arugula. They all have yellow to white blossoms, sometimes pink, usually a simple cross which is there the family names Cruciferae comes from. They range from the Mustard that produces the seed that makes the condiment to the radish in our salad to the plant that produces what eventually is cleaned and deodorized into Canola oil. In northern climates they are a spring and summer plant, here in Florida they are wintertime fare, showing up after Thanksgiving and usually totally gone by St. Patrick’s day. Wild radish and wild mustard look similar but have small differences. One is that Mustards grow tall, radishes like to serpentine. Radish blossoms cluster and have noticable veins, mustard blossoms are singular and the veins are not obvious. The seeds pods are different as well. Mustard’s pod is smooth, the radish jointed and why the mustard is called the charlock and the radish the jointed charlock. Their blossoms are both peppery and mustardy. They work best in cold salads or hot soups, the latter they can be tossed in just before serving. And of course Mustard and radish leaves can be cooked up as greens.
Perhaps I have been remiss not mention Mustards more. But they are a huge family and have been touched upon, such as with arugula. They all have yellow to white blossoms, sometimes pink, usually a simple cross which is there the family names Cruciferae comes from. They range from the Mustard that produces the seed that makes the condiment to the radish in our salad to the plant that produces what eventually is cleaned and deodorized into Canola oil. In northern climates they are a spring and summer plant, here in Florida they are wintertime fare, showing up after Thanksgiving and usually totally gone by St. Patrick’s day. Wild radish and wild mustard look similar but have small differences. One is that Mustards grow tall, radishes like to serpentine. Radish blossoms cluster and have noticable veins, mustard blossoms are singular and the veins are not obvious. The seeds pods are different as well. Mustard’s pod is smooth, the radish jointed and why the mustard is called the charlock and the radish the jointed charlock. Their blossoms are both peppery and mustardy. They work best in cold salads or hot soups, the latter they can be tossed in just before serving. And of course Mustard and radish leaves can be cooked up as greens.

Nasturtiums are peppery
Nasturtiums are a favorite nibble of my mother. We always had a row or two of them growing every year. The blossoms are peppery. In fact, the entire plant above ground is edible, even the seeds which can be pickled and used like capers. Nasturtium in Latin mean literally to twist the nose, because of their pungency,. They have have been praised for their flavor for at least 2,000 years. Multi-colored, low growing or trailing, Nasturtiums are often used in kid projects because the seeds are large, they’re fast to germinate and grow, safe, and edible.

While we’re raiding the garden let’s not forget about Okra blossoms. Like many edible flowers already mentioned it is in the hibiscus clan. I have grown Okra in my garden and there are dozens of cultivars to choose from that produce some variety of blossom colors. Like most hibiscus blossoms they are shy on taste but add color and texture to salads as well as an attractive garnish. Of course you could also let them go on to produce Okra which is a kitchen vegetable of many uses. In fact, growing Okra is for the blossoms is perhaps the quickest and easiest way to get lovely large blossoms to your table quickly. And there are “dwarf” version for patio pot use. One word of warning, some Okra plants have spines.

There are some 400 species in the Allium association if you include Onions, garlic, chives, sallots, and closely related ramps/leeks, the latter having wide leaves. Usually the flowers have a stronger flavor than the leafy parts, and the developing seed head even stronger flavor. Blossoms are usually white but can also be pink. Onion stems are round, as are chives but smaller. Garlic leaves are flat. Ramps and leeks have large leaves.

Tap to dislodge bees first
I have read there are no toxic Opuntias. With some 300 of them I don’t personally know. I do eat cactus pads on a regular basis. I fry and grill them. But, as with most cactus, one has to contend with glochids and spines. The spines one can see. It’s the tiny hair-like glochids that can make one semi-miserable, tolerable in a finger, maddening in your tongue. Duct tape removes them moderately well. Wear gloves harvesting. The best approach is to use a long shap fillet knife as the flowers are surprisingly thick. Also tap them first to dislodge bees. Among all the Opuntia the Prickly Pear Cactus flower is the most often eaten, not raw but cooked, usually boiled. Their flavor leans towards tart. The blossoms also make a good wine.

Where would Greeks be without Oregano, or the rest of us? And is it a wild plant or cultivated? In most of the New World it is a cultivated plant. In the land of my ancestors it grows wild, particulary on the lopes of Mt. Taygetos (said tah-EE-gah-tos) south of Sparta in The Mani (and from where we get the word maniacs in English because of how the Maniotes fought.) Taygetos means “joy of mountain.” Oregano is similar. It’s from two Greek words, oros, which means moutain, and ganousthal meaning delight in. “Delight in the mountain is” translated into good eats and where the oregano prefers to grow. There should be some truth to that because oregano also grows in Sanmaria Gorage on mountainous Crete, where I love to hike. We are told Aphrodite, the goddess of beauty, created oregano as a symbol of happiness. Ancient Greeks would crown newlyweds with garlands of oregano to bless of happiness on their marriage. Oregano’s blossoms are a milder version of the plant’s leaves Incidentaly, majoram is in the same genus as oregano. Oregano is Origanum vulgare, and marjoram is Origanum majorana. Think of majoram as oregano lite and used the same way. In many place in the Mediterraean area Oregano is called Wild Majoram.

The problem with Pansies is the same problem with Begonias: Getting them from a wholesome source. Pansies are actually violets and descended from the much-loved Viola tricolor aka Johnny-Jump-Ups. There is always the question if one should lump all violets in together or do some sorting. I chose to sort a little. Pansies are extremely common bedding plants but they are commercially raised so that can mean some chemicals you don’t want to consume. It is best to raise your own so you know exactly what you’re eating. Like most short violets pansies tend to have a nice scent and are sweet to the taste. There are only two cautions. Violet roots are definitely not edible. The American natives used them for insecticide. And, yellow violets tend to be laxative in less than moderate quantities.

Female papaya blossom
This won’t make much sense to those who live where there is a winter but the first time I climbed Turtle Mound — not a great feat as it is only 80 feet high — I was surprised to see Papaya’s growing on top. Turtle Mound is a midden, an ancient trash heap made mostly of millions of oyster shells dumped there by ancient natives. It’s been more than three decades since my first visit and the papayas are still there, self-seeding as papayas do. A native of Mexico they are naturalized in warm areas of the world. Papaya blossoms, like very young leaves, are edible cooked, which is usually by boiling. Actually cooking the yellow flowers is a lot easier than pollinating them because there are female blossoms, male blossom, and male/female blossoms, kinda you, me and us. You have to move pollenating material around correctly or you don’t get fruit (also edible.)

Parsley Flowers
Like so many of our spices Parsley is a native of the Mediterranean. While for this article we are interested in the flowers there are actually two major divisions within the parsley realm, leaves and roots. Among the leaves there is curly or flat leaf. Interestinlgy the flat leaf is closer to the wild parlsey than the curly. Flat leaf is easier to grow, more tolerant of agricultural abuses, and has a stronger flavor. Curly leaf is more decorative and milder in flavor. It is the one used mostly for a garnish. There is also a root parsley, not common outside of central and eastern Europe where it is used in soups and stews. It has a nutty celery/parsley taste and is often fried like potato chips. From Argentine salsa to a tea Vitamin C rich parsley has multifold uses in the kitchen. Even the stems can be dried and added to dishes. The blossoms are salad fare or can be added to anything the leaves are used for. Parsley, incidentally, means “forked turnip” though parsely and turnips are not related.

There is a progression, I think. When you are a kid you hate to eat your Peas. You get past that then run into your first peapod, usually at a Chinese restaurant. You get past that when you eat your first pea blossom. Note, eating pea blossoms will reduce your production of peas but a pea blossom here or there is pleasant. They are crunchy, slightly sweet, and taste like peas. That does vary some with what varity you have planted. Also the pea shoots and tendrils are edible as well. All usually consumed raw though you could cook them. A word of caution. I am referring to edible peas, the genus Pisum, not ornamental peas. Those can be toxic.

When my father passed on six years ago he left a small Peony garden that still has 18 bloomers, one red and a wide variety of pink shades. They’re quite hardy and don’t like to be moved. Peonies have been been cultivated in home gardens since about the time Columbus sailed the ocean blue. Of course there are no good ones where I live because they like temperate climates and need winter chilling. Originally from China they were and still are used for medicine. Petals can be added to salads or will happily float in drinks. Another option is to parboil them, add a little sugar, and use them as a sweet treat.

Petunia x hybrida
One wouldn’t think so but there is an edible Petunia species. Petunias are in the solonace family which has some famous edibles and poisons. This is not just any petunia but Petunia x hybrida probably developed in the early to mid-1800’s. The P. hybrida was created out of several Petunia species and comes in two types, grandiflora (large flowered) and multiflora (many flowered.) Grandiflora have trailing stems and tend to spread with blossoms up to five inches. Multiflora petunias are bushier and have smaller flowers from two to three inches in diameter. Many colors and patterns are available. The mild-tasting flowers are used in salads or as a garnish.

There are two Phlox, so to speak. One that gets one to two feet high and shows up seasonally in fields, particularly here in Florida. That’s not the one you want. You want the perennial phlox that grows to three of four feet tall, Phlox paniculata. I’m sure you’ve seen it. Like the Meadowsweet above it is an old world plant found in many home gardens and yards. It has escaped into the wild and can be found in the eastern half of North America plus Oklahoma, Kansas, Nebraska, Utah and Washington state. The slightly spicy blossoms range from red to pink to white. They go well with fruit salads.

Pineapple Guava’s are becoming a popular ornamental with an unusual flower and fruit. In fact, there is one where I teach regularly. The blossoms are striking and reminds one of several cactus blossoms, in its own way. The fruit, equally unusual, ripens in September or October here. It stays green but does get soft enough to eat. There is a bit of pineapple in the fruit’s flavor if one uses the imagination. I have a Strawberry Guava in my yard and its even more difficult to taste “strawberry” It’s fruit. The flower of the Pineapple Guava, Strawberry Guava, sweet. Like the fruit it says tropical reminding one of papaya.

Our next edible flower comes with a warning. Don’t eat its similar looking realitive. How can you tell them apart? The one you want smells of pineapple, which is why it is called the Pineapple Sage, Salvia elegans. Sometimes it is also called the Tangerine sage. The point is crush a leaf and you will smell pineapple or tangerine. The one you don’t want is Salvia coccinea, also called the Scarlet Sage, the Texas Sage and the Hummingbird Sage. Crush its leaf and it smells grassy or slightly sage-like. Flowers of the Pineapple Sage, which taste like a hint of pineapple, are quite edible. However, even a quarter-inch square portion of a Salvia coccinea blossom will give you a big stomach ache and make you more than mildly ill. It’s not go-to-the-emergency-room ill but close to it. I know this from personal experience beause once, for lack of a better word, I titrated the S. coccinea for potental edible use. It quickly let me know it is defintely is not an edible, raw at least. After my experience I had no interest in seeing if S. coccinea had any uses cooked.

Carnations (Dianthus caryophyllus) were covered above but let’s revisit the genus Dianthus minature version such as Pinks and Sweet William, respectfully Dianthus plumarius and Dianthus barbatus.) Dianthus means God Flower… Hmmm… would diandros be godfather? Anyway… These little carnations don’t like heat or alkline soil which made them perfect for the cold acidic landscape of Maine’s summer. They don’t even like to be mulched. Curiously the name “Pink” does not refer to the color but a 14th century verb “to pink” meaning to preforate or create a punched patten. Apparenlty I grew up in the Dark Ages because it was a verb I heard around the home. Why Sweet William is called that is anyone’s guess but the term for the flower first showed up in 1596. (There were no King Williams at the time but William Shakespeare was mid-career… it’s a guess.) To use the blossoms cut away the bitter white base. The petals are sweet with a clove or nutmeg like scent. Often used in salads, aspic and soups.

How many Hosta’s there are is a matter of taxonomic debate. Maybe 45. While the flowers of all of them are reported to be edible, according to the Montreal Botanical Garden, at least the young leaves of one, Hosta lancifolia, the Narrow Leaf Plantain Lily, are eaten cooked or preserved in salt. It’s a common home and landscaping plant that can tolerate shade and has naturalized in several states from Massachusetts to all states touching a straight line west to Indiana. I’m sure you have seen its distinctive leaves. It’s a good thing you are interested in the flowers because just about every woodland creature loves to eat the leaves, from deer down to insects. In temperate climes look for blossoms at the end of summer or early fall.

The Primrose suffered the fate of several plants. Petty, edible and showed up very early in the spring after folks had spent a long winter with no fresh food. This wasn’t an issue when there were more primroses than humans. The primrose as been so harvested in the wild that it is not illegal in many of its native places in Europe to pick it. However, it is also a common garden flower and a commerial product so getting some primrose legally really isn’t an issue. In the genus Primula vulgaris the blossom reminds me of a small magnolia blossom. Several colors are avaiable now. Also know as Cow Slip the blossoms are bland in flavor but sweet. The can be added to salad, the bud picked, or cooked as a vegetable. They have even been used to make wine.

Long ago and far away I got accepted to law school. The job I had stopped before classes began so to tide me over I delivered flowers. One could tell several stories regarding that including how most women are very suspicious when they get Roses from him other than Valentine’s Day. I even had some deliveries refused! Beyond that, however, the roses I delivered had no scent. None. Zip. Zilch. Nada. No rose aroma at all. Just before I would deliver them I’d take them out of the van and spray them with an artificial rose aroma. The roses were raised for their look and in the process the scent was bred out (and you did not spay them in the van or you smelled roses for weeks.) Less purebred roses are known for their rosehips and edible petals. The flavor depends on the type, color and conditions of raising. They can range from tart to sweet, spicy. Darker ones have stronger flavor. Remove any white portion of a petal. That will be bitter. All true roses (genus Rosa) are edible.

Rose of Sharon
South Korea is crazy about the Rose of Sharon, Hibiscus syriacus. It’s their national flower. It is on everything, and it’s native to Korean and much of Asia. So why is it called syriacus, which means “from Syria.” They got it wrong a few centuries ago. They thought it was from Syria. Oddly mistakes like that cannot be changed. That it is wrong in not enough. There has to be a botanical reason to change a plant’s name once given, not a geographical one. Called mugunghwa in Korean — which translates into “flower of eternity” or something close to that, been a garden staple in that country since there were gardens — hence the eternity spin. The leaves are made into tea and the flowers eaten, usually raw. It made it to Europe by the 1500s and was in most English gardens by the 1700s. The American colonies followed suit. It’s also my mother’s favorite flower. Had to mention that or I wouldn’t hear the end of it.

I can remember the first time I saw Rosemary growing in the wild in North America. I was on a business trip to California. Of course it grows wild in its native Greece. There it is called ???????????? (then-dro-LEE-vah-row.) Students in ancient Greece wore it around their necks in garlands or braided it into their hair thinking it improved their memory. In English Rosemary means “remembrance.” I have two bushes of it growing in my yard. The light blue blossoms are sweet, spicy, pungent and taste of rosemary.

Safflower
Because saffron is so expensive, $100 to $150 an ounce, several flowers have been used as substitutes and adulterants, among them Safflower. But, safflower has uses in its own right. Botanically Carthamus tinctorius, safflower blossoms are the source of a yellow or red dye used in butter, confections and liqueurs… and you thought that Sambuca was naturally colored… The seeds are fried and eaten in chutney. The oil is used in salads and cooking. Young leaves can be eaten as a potherb or seasoned in soy sauce. The flower’s petals are edible, slightly bitter, often cooked with rice.

Three “saffron” stigmas
As of this writing the best price I can find on the Internet for saffron is $92.95 an ounce, free shipping, marked down from $144. Why is it expensive? Because “saffron” is the three red stigmas of the flower and must be picked by hand. Limited amount, labor intensive. It is the most costly spice by weight. Then again, one uses very little of it. Saffron is acually a crocus, Crocus sativus. It does not grow in the wild and is totally cultivated by man. Technically it is a monomorphic clone and believed to be a mutant form of Crocus cartwrightianus. The Greeks were the first to cultivate it, probably on Crete. Historians tell us it has been bought and sold for over four thousand years. Ninety percent of the world’s saffron comes from Iran. The styles are used to flavor and color sauces, creams, breads, preserves, curries, rice, soups, caked, puddings, eggs even butter and cheese. It can be a tea substitute and the roots roasted. It’s not a spice you keep on hand. Usually purchased for a dish specific. It takes about 13,125 dried stigmas to weigh an ounce. Oh, I forgot to mention: In large amounts saffron is deadlly. That’s an expensive way to go.

Scarlet Runner Bean is not your run-of-the-mill bean. It has bright red flowers, multi-colored seeds and puts on a root to be a perennial though most folks view it as an annual. Depends where you live, I suppose. The root is edible, the young pods are before they get fibrous, and the beans in or out of their pods are edible either cooked fresh or after shelling and drying. Read the beans have to be cooked no matter how you prepare them but young pods don’t. The blossoms are under an inch across, grow in clusters, and are available all season. The flavorful flowers are favored by hummingbirds and butterflies and make excellent garnishes for soups and salads. There are at least 18 varieties of the Scarlet Runner Bean. Usually the vine is used to cover fences, guy-wires and trellises.

Snapdragons
While most articles on edible flowers include Snapdragons I considered leaving them out. Let me put it this way: If the flavor of the Snapdragons existed in some other plant it would not be eaten. They are edible, they won’t kill you, but when it comes to flavor they are on the poor to bad side. Their taste can run from bland to bitter, depending upon the soil and how they were raised. They get included on edible flower lists — particularly the commercial edible flower list — because they are pretty, a lot of folks recognize or grow them, and few people eat garnishes anyway. If you ever draft a list of edible flowers and you aren’t alphabetizing, put Snapdragons last, better still, as a Post Script, a little asterisk at the bottom. The genus they are in is called Antirrhinum. It’s Greek and means “opposite the nose” or “unlike the nose.” I don’t know why that family is called that but I am sure it is not a compliment. They are called “snapdragons” because of the blosom’s resemblance to a fictional face of a dragon that opens and closes when squeezed.

It’s clearly not wild. It’s clearly a planted ornamental. But I get asked about it all the time. Is Society Garlic edible? The short answer is yes. The blossoms smell and taste far more like a vegetable than a blossom. Their flavor is sweeter than garlic, more like of an onion but still peppery. They’re actually a native of South Africa and only a distant relation to regular garlic. White settlers to South Africa considered it a more polite spice to eat at social functions than real garlic. It’s probably safe to say that there is more Society Garlic growing locally than real garlic. Garlic does not like the hot weather whereas Society Garlic thrives in it. If they are well-established they are drought resistant. The leaves are also edible, and are the bulbs on many species. Use the flowers in salads or soups, anyplace you want a bit of garlic, pepper and onion. I have a separate article on them on site.

Squash blossoms actually cover a wide range of flowers. Zucchini, pumpkins, calabashes. All are squashes for our purposes and all have edible blossoms. Both male and female blossoms are edible but removing female blossoms can reduce squash production in your garden. You can tell the female Squash blossom by looking just behind the blossom. There you will see a miniature Squash or the like. Stuffing Squash blossoms with soft cheese is a time honored means of preparation. What people don’t know is that the leaves and sprouts of most garden variety squashes are edible cooked as are their seeds. Removed the seeds, wash off the debris, and roast in a slow oven for a half hour or so. You can eat them shell and all or shell them.

Stock is bred in many colors
Some like it hot, and some do not, and Stock does not. It’s a fragrant, two-foot tall, attractive flower that likes full sun, good, well-drained soil, and temperatures under 75F. They can even tolerate a light frost. There are some 140 species of Stock. The one we are interested in is Matthiola incana, common stock as it were though it comes in many colors. It’s native along the Mediterranean from Greece to Spain and was a mainstay of European gardens in the 16th and 17th centuries. The Elizabethans called them “gillyflower” and the Victorian allowed them in their cottage gardens. Even Thomas Jefferson got some for Monticello in 1771 and in fact one can still buy seed from Jefferson’s stock. Stock flowers are usually added to salads eaten raw or a garnish with sweet disserts. They can be candied. Their flavor is perfume-ish. The flower’s pods are edible, too. A common cultivated flower in North American it is naturalized in North Carolina, Illinois, Texas, California and British Columbia usually in a few isolated areas but rather well-distributed in coastal southern california and San Francisco. It is also called Tenweeks Stock.

Strawberry Blossom
There’s a real good reason why almost no one knows this next flower is edible. And that’s because nearly everyone eats the fruit! Strawberries are prime food. Botanically Fragaria ananassa, Strawberry blossoms are edible raw though most folks wait for the fruit. Of course, you can be different and toss the flowers on salads just to surprise folks. The leaves are edible as well but are on the astringent side. As with many cultivated crops harvest carefully because as a commercial crop they are often doused wth this or that chemical to keep them living and looking well until they get to market. The cultivated blossoms are pink, the wild white.

Sunflower petals are edible
Nearly everyone knows you can eat Sunflower seeds. There are actually two general kinds of seeds. There are black seeds with a white stripe. Those are the ones you usually buy in the store. Then there are Sunflower seeds that are smaller and totally black. Those are used for oil (and those that don’t make the oil grade end up in bird seed.) But there’s more to eat on a Sunflower that seeds, no matter which kind. The unopened buds are edible cooked. They taste like artichokes, to whom they are closely related. And once the huge blossom is open the petals can be eaten, though they are bittersweet. The petals are often mixed with pasta.

Szechaun Buttons
Szechaun Buttons, Paracress. No, they’re not from China but Brazil. This is an edible flower you will likely want to grow yourself rather than order. Right now a 30 blossom order is selling for $39.95 not including shipping. Why would you order them? Because they are the current party favor but they have other uses as well. Spilanthes acmella, aka, Acmella ocleracea, grow in Brazil. They are peppery like capsaicin, hence their name because of a heat similar to Szechuan peppers… well almost. The active chemical is spilanthol. That used to numb gums for toothaches. It causes a reaction with the trigeminal nerve pathway controling the control motor and sensory functions of your mouth. The result is a tingling, popping sensation in the mouth. Kind of a cross between Pop Rocks and a 9-volt battery. Besides that, they are cooked and used in salads, sauces, soups, sorbets and as cocktail garnishes. You can add shredded uncookled greens to your salad, sparingly, or sprinkle some uncooked petals on your salad. The taste is herbal and slightly bitter. One high end restaurant uses them in a cheese plate. At another the tiny petals and some lemon thyme are infuse a small pot of honey that accompanies roasted kabocha squash, sweet peppers and toasted walnuts. A third offers patrons a Concord grape soda float with lemon verbena sorbet into which shreds of Sechuan buttons are dispersed through a soda siphon. Did I mention they use Szechaun Bottons to flavor chewing tobacco in India?.

Another escapee from Eurasia now found over most of North America and the rest of the world is the Common Tansy. First mentioned for medicinal uses by the Ancient Greeks, the “bitter buttons” by the 8th century were in Charlemagne’s herb gardens and used by Benedictine monks in Switzerland. In 16th century England it was a “necessary of the garden.” Tansy, related to the thistle, even been used as an insect repellent. In fact, meat (and corpses) were wrapped in it for preservation and keep insects at bay. It is not a good repellent against mosquitoes but does a good job with the Colorado Potato Beetle. Like chamomile it contains thujone so it should be used very sparingly. But then again, that’s what spices are for. The blossoms’s flavor is bitter, camphor-like.

Tea Blossom
Our next plant is known by billions. Wars were fought over it, an empire build and fortunes made, Camellia sinensis, better known as Tea. Yep, the tea in your cup. When I first bought land I planted a C. sinensis knowing it was iffy. It was. Didn’t make it. Too warm, too humid. And it is an understatement to say tea change the course of history. Read about Robert Fortune in my article on Forsythia. He was sent by the British government to China, undercover, to steal tea seeds and the like to start a tea industry in India, a thef and resulting Indian tea industry that China has only recently surpassed. Besides a beverage, tea makes a marinade for fish and meat, mixed with anise blossoms it is used to make “tea eggs.” Kombucha is basically tea cider, leaves are used to smoke meat, its fruits are eaten, leaves are chewed to remove the odor of garlic and onions, and the blossoms are cooked. One favorite way is to make tempura out of them, deep frying them.

Tea Olive
If you go to an Asian market and buy “Cassia Blossom Jam” it is not from the Cassia clan at all but rather Osmanthus frangrans, the Tea Olive, also called the Fragrant Olive and Sweet Olive. Its name(s) gives you a good idea what it is used for. It a glossy evergreen with little white blossoms that bloom almost all year long, making it a favorite landscape plant where it is warm all year. The blossoms smell deliciously fragrant or ripe peaches or apricots. It tends to bloom in autumn, winter and spring. Fruit follows about six months later. The unripe fruit are preserved in brine like olives. The flowers are used to make tea fragrant as well as wine, liqueurs, and confections. The blossoms are either preserved in a salty bring or made into a sugary paste. The Osmanthus americana, the American Olive, is used a similar way.

Thyme
I went to Crete in the spring once to longest gorge in Europe if you count extreme southern Greece as geographically part of Europe proper. There was, however, a late season snow storm and the gorge was closed. So I hiked down Embrose Gorge, much smaller but not without its charms. I remember three things well from the hike. The first was the wonderful scent of wild thyme growing throughout the gorge. Next was literally being run over by a large heard of sheep and goats. And lastly later that evening discovering the local taverna-made rose smelled just like the sheep. Without thyme the chef and the herbalist would be hard pressed to find a suitable substitute. In the kitchen thyme has so many use including the blossoms. Thymus vulgaris, leaves and blossoms are used to flavor stuffing, fish, meat, fowl, cheese vinegar, gravies, sauces, bouquest garni, herbs de Provence, brine for olives, eggs, bread, tea and honey. Shoots are a garnish. The blossoms are milder than the leaves.

Tuberose has been put to a lot of uses. The Hawians used it to make leis. In Victorian times it was the funeral flower of choice. Then it spent a long time helping perfumes smell the way they do. Now it can be found as a food in five star hotels, well… at least those in the Orient. Botanically it is Polianthes tuberosa and might be a native of Mexico.The flowers open from the bottom of the flower spike up and can last a couple of weeks if you remove the blossoms and eat them. The Aztec so liked the flower their used its oil to flavor their chocolate. They are eaten cooked and are traditonally added to vegetable soups. They are also used to flavor some soy sauces

Tulips’ flavor vary with color
Tulips are one of those wonderful flowers you hear that is toxic. The answer is yes and no. The petals are quite edible raw or cooked though they loose their color on cooking. They can have many flavors: Bland, beans, peas, and cucumbers. Pink, peach and white blossoms are the sweetest, red and yellow the most flavorful. While you can use them to garnish salads their more common use is to hold appetizers or dip. If you use the entire blossom cut off the pistil and stamens from the center of the blossom. The bottom ends of the petals can also be bitter so cut them off as well when used individually. So what is toxic? The yellow inner core of the tulip bulb. It has to be cut out before the rest of the bulb can be cooked and eaten. Also know some people are quite allergic to tulips

Wisteria is a nibble of spring, here for a few weeks and then gone. The blossoms of various species are edible cooked — some raw — but they are usually blanched in boiling water, strained, and mixed into salads or the deep fried. The rest of the plant is toxic per se. In fact, as little as two raw seeds can kill a child. That is not uncommon for a member of the pea family which ranges from edible to toxic. See my full article on wisteria on this site for edible variations. One of the most common of the 8 to 10 species of wisteria is Wisteria sinsensis, or the Chinese Wisteria. It’s a vigorous, fast grower that doesn’t need fertilizer and fixes nitrogen. In fact, abuse improves blossoming as does pruning. It can live at least 115 years (as of April 2011) and is consider an invasive species is some areas. It has naturalized from Maine to Florida and as far west as Arkansas. Not bad since its arrival in 1816. Another one commonly eaten wisteria is Wisteria floribunda from Japan, also escaped in the US.
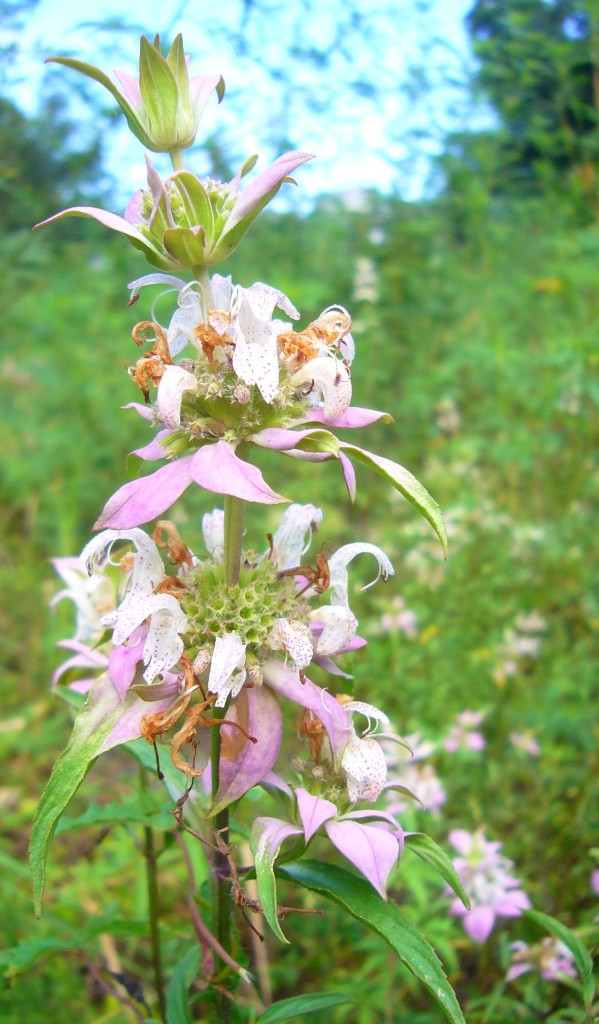












 Crowfoot Grass
Crowfoot Grass