

Fresh lotus seeds from a mature green seed pod. Photo by Green Deane
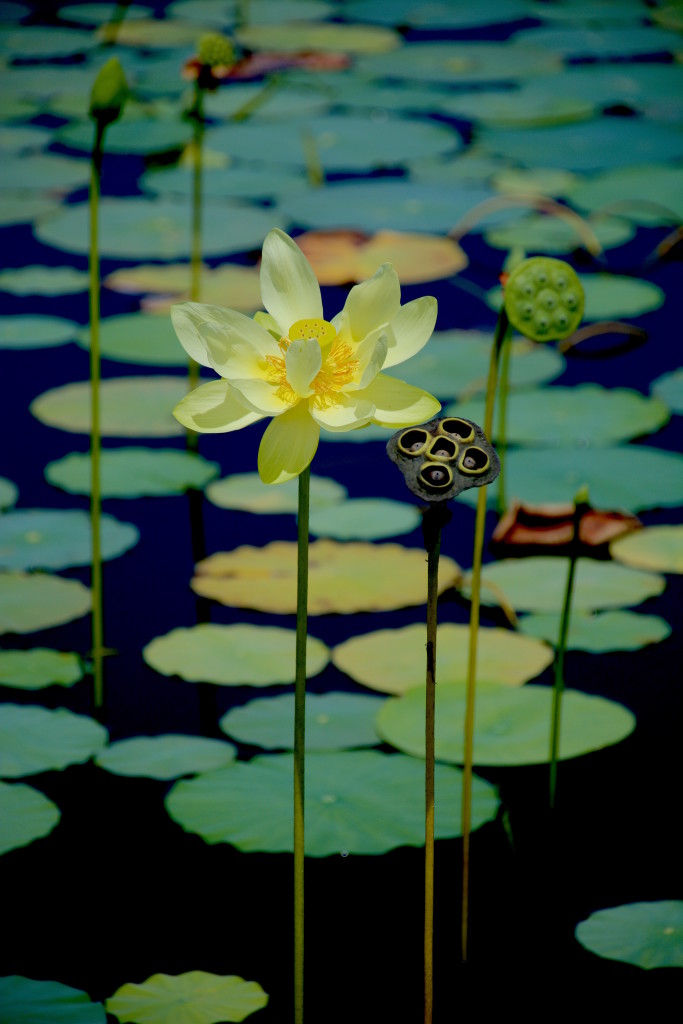
Yellow ponds, that’s how I think of it, or in some places, yellow rivers. That’s because the American Lotus is in blossom. The first time I saw a small lake of these blossoms was when an old dry lakebed was deepened for a housing development. The next spring suddenly what was for decades a dry lake was full of American Lotus blossoms. This is because the seeds can stay viable some 400 years, or so the experts report. Talk about a survival food! There are multiple edible parts on the American Lotus but I prefer the seeds. I also think when collecting by hand the seeds proved to be the most calories for the least amount of work. The roots are edible but digging them up can be a messy, laborious job. Locally American Lotus are easy to find now: Just look for a lake with large yellow blossoms on long stems. Further north and west they are a favorite sight on rivers such as the Mississippi. To read more about the American Lotus go here.

Jack in the Pulpit. Photo by Green Deane
Jack In The Pulpit are strange plants. They’re listed amongst the edible species but barely. One unusual aspect about the species is they readily change sex. After reproducing they become males and do nothing but hang out on the forest floor drinking sunlight and making starch. When enough energy has been collected for reproduction — three or four years — they become females… It’s not a species that does much dating. They like damp, sun-dappled places. We see them often during foraging class in Jacksonville. They are also common along the bike trail through Big Tree Park in Sanford. To read more about Jacks and my microwave experiments with them you can go here.

Black Cherries are both bitter and sweet.
Black Cherry has been mentioned a couple of times earlier this year and that’s the reason for it being mentioned now: It’s still fruiting. The season seems a bit longer this year than usual and I still see them here and there. It is safe to say Black Cherries look better than they taste. There is an initial cherry sweetness but then a residual bitterness takes over whereas chokecherries are bad start to finish. There were four of those trees on the other side of our lawn where I grew up in Maine. They were quite irritating: They looked wonderful but tasted awful (unless made into wine.) Black Cherries, like the chokecherries, are much better processed into jelly and jwine (or cough medicine from the bark.) Do not eat the seeds. To read more about the Black Cherry go here.

The Toxic Atamasco Lily. Photo by Green Deane
What are they? The first answer is they are NOT edible. The second is they are a threatened species. And the third answer is they are the toxic Atamasco lily, aka Rain Lily ( Zephranthes atamasca.) For a threatened species they are seen in a lot of lawns this time of year prompting many emails asking for an identification. These natives like wetlands but a well-watered lawn after seasonal rains will do nicely. The problem with the Atamasco is that it resembles wild garlic before it blossoms (and even has a bulb!) However, it does not have the telltale garlic aroma. Remember if it smells like a garlic AND looks like a garlic you can use it like a garlic. The Atamasco does not have any garlic/onion aroma. It is not edible. All parts are poisonous. Leave it alone. And while these in the picture have a pink tinge there are also all-white blossoms.

Edible fat and toxic oil all in one seed.
During a class recently I noticed the Chinese Tallow trees are blossoming. The tree poses a challenge. It has an edible fat and a toxic oil. The question is how to easily separate the two. And if “easily” is the wrong descriptor then how can it be made worth a forager’s while? The tree, Triadica sebifera, is an invasive species locally so finding a use for it would help the environment. Also as a source of fat it could literally be a life-saver in time of need because humans cannot survive without fat. In fact one can readily see the white fat (also called wax) on the seeds. It just doesn’t render easily. Each seed has a thick coating of highly saturated fat, one reason why the species is also called the popcorn tree because when in fruit it looks covered by popcorn. By all reports the outer coating is edible and has been used to make candles, hence calling it wax. In fact the tree was imported from Asia by Ben Franklin specifically to start a candle-making industry in the South. As a saturated fat the outside is very solid at room temperature. Inside the seed is a liquid oil called stillingia. It is toxic to humans.

Chinese Tallow seed oil is toxic.
The “wax” is supposed to melt at 104 F. I’ve tried frying the fruit. The outer coating of fat stays solid. I’ve tried boiling. No luck. My readers have tried broiling — the seeds exploded — and micowaving, they got softer but did not melt. In China they soften the fruit in boiling water than scraped them over a fine grater. Separating the fat and the oil was also a science project. Here’s what the student did. First she bought a hand-operated oil expeller. They cost about $150 on the Internet. She put the entire fruit through the press which also heats the material. Out comes a liquid mass that upon cooling has the solid saturated fat on top and the oil on bottom. She went on to make candles out of the “wax” and used the oil in a lamp which won her three science fairs and two scholarships. Way to go! The next question we ask is whether the “wax” (saturated fat) and the oil will sufficiently separate so the fat can be used as food? Also is it just as stubborn to melt even after being processed this way? My last question would be how digestible is it? The invasive species certainly has a lot of potential. You can read more about the Chinese Tallow tree here.

Classes are held rain or shine or cold. Tropical storms and hurricanes are exceptions.
Two foraging classes are scheduled for this weekend if the weather cooperates. Rain and wind is no issue unless it reaches tropical storm status. We’ll just have to watch the weather.
Saturday, June 6th, Colby-Alderman Park: 1099 Massachusetts Street, Cassadaga. Fl. 32706. Meet at the bathrooms. 9 a.m. to noon.
Sunday, June 7th, George LeStrange Preserve, 4911 Ralls Road, Fort Pierce, FL, 34981. 9 a.m. to noon. This location does not have an official bathroom.
Saturday, June 13th, a mushroom class in Lake Mary, FL., 9 a.m. to noon. Details to follow and on Orlando Mushroom Group facebook page.
Sunday, June 14th, Blanchard Park, 10501 Jay Blanchard Trail, Orlando, FL 32817. Meet at the pavilion between the YMCA building and the tennis courts. 9 a.m. till noon.
Saturday June 20th, John Chestnut County Park: 2200 East Lake Road, Palm Harbor, FL 34685. Meet at the trail head of the Peggy Park Nature Walk, pavilion 1 parking lot. 9 a.m. until noon.
Sunday, June 21st, Bayshore Live Oak Park, Bayshore Drive. Port Charlotte. 9 a.m to noon. Meet at the parking lot at Bayshore Drive and Ganyard Street 9 a.m. to noon.
For more information, to pre-pay for a class, or to sign up go here.

Maypop blossom and unripe fruit. Photo by Green Deane
It’s June and Maypops are popping out all over. They are easy to find: Look for a vine that has three-lobed leaves and smooth, green fruit shaped like a large egg to a tennis ball. The fruit ripens to yellow near the base of the vine first. The plant, which smells like an old gym shoe, will put on new fruit until cold weather. Green fruit can be fried like green tomatoes. Sometimes the green ones have seeds mature enough to be tart. Sweet and sour seeds can be scooped out of the yellow fruit and eaten along with their white jelly-like coating. Locally our most common passion fruit is Passiflora incarnata, left. You will read on the Internet that it contains cyanide. It does not though many passion fruits do if not all but P. incarnata. It was specifically tested and definitely does not have cyanide in it’s leaves. The varying amounts of cyanide in other species of passion fruit is one reason why animals don’t eat them and one reason why you should not eat any ornamental passion fruit you may have. Instead of cyanide P. incarnata has GABA, gamma-Aminobutyric acid, which calms you down.

Green Deane videos are now available on a USB.
Changing foraging videos: My nine-DVD set of 135 videos has been selling for seven years. They are the same videos I have on You Tube. Some people like to have a separate copy. The DVD format, however, is becoming outdated. Those 135 videos plus 15 more are now available on a 16-gig USB drive. While the videos can be run from the DVDs the videos on the USB have to be copied to your computer to play. They are MP4 files. The150-video USB is $99 and the 135-video DVD set is now $99. The DVDs will be sold until they run out then will be exclusively replaced by the USB. This is a change I’ve been trying to make for several years. So if you have been wanting the 135-video DVD set order it now as the price is reduced and the supply limited. Or you can order the USB. My headache is getting my WordPress Order page changed to reflect these changes. We’ve been working on it for over three weeks. However, if you want to order now either the USB or the DVD set make a $99 “donation” using the link at the bottom of this page or here. That order form provides me with your address, the amount — $99 — tells me it is not a donation and in the note say if you want the DVD set or the USB.
Green Deane Forum
Want to identify a plant? Perhaps you’re looking for a foraging reference? You might have a UFO, an Unidentified Flowering Object, you want identified. On the Green Deane Forum we — including Green Deane and others from around the world — chat about foraging all year. And it’s not just about warm-weather plants or just North American flora. Many nations share common weeds so there’s a lot to talk. There’s also more than weeds. The reference section has information for foraging around the world. There are also articles on food preservation, and forgotten skills from making bows to fermenting food.
This is weekly newsletter 408, If you want to subscribe to this free newsletter you can find the sign-up form in the menu at the top of the page.
To donate to the Green Deane Newsletter click here.


Hi, Deane, are the spinach leaves with white tracks on them edible?